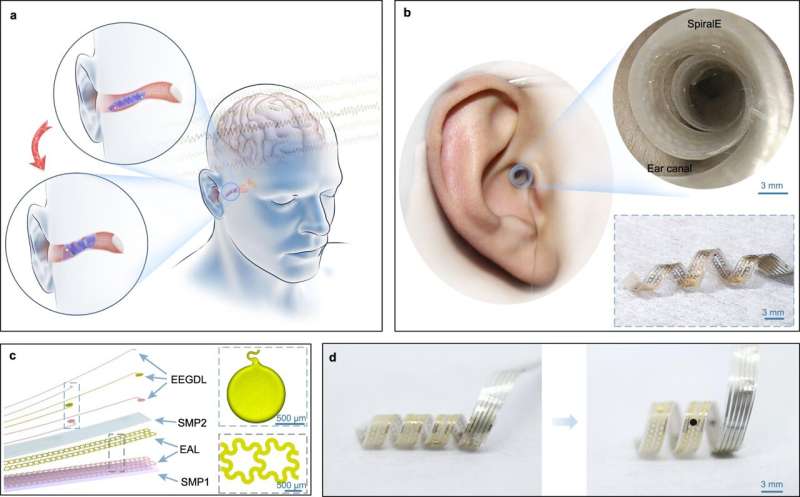
A multi-institutional team of engineers in China has developed a new type of brain-computer interface (BCI) that can be easily slipped in and out of the ear canal. In their project, reported in the journal Nature Communications, the group set out to design and build a new kind of BCI that is less invasive than existing devices.
A brain-computer interface is a device that allows communication between the brain and a computer—though to date, most such devices are one-directional. They are used to listen to brain waves for such applications as converting them to text or to electronic signals that can be used to engage another device, such as a wheelchair.
One of the main drawbacks of most BCIs is their invasiveness. Current approaches involve the use of electrodes attached to the scalp, or microneedles or probes that pierce the skull. In this new effort, the team in China has built a BCI that is not only less invasive but can be engaged and disengaged easily.
The new, corkscrew-shaped BCI is called the SpiralE. It is engaged by gently screwing it into the ear canal and disengaged by doing the reverse. It is made mainly of soft material to ensure comfort for the wearer. The design allows the passage of sound waves, ensuring that it does not impair hearing. The soft material comprising the body also prevents echoing inside the spiral.
The research team suggests that the SpiralE could open the door to new BCI applications due to its ease of use. They envision the development of applications that convert full thoughts into text, controlling objects in both the real and virtual worlds—and even perhaps augmented memory.
More information:
Zhouheng Wang et al, Conformal in-ear bioelectronics for visual and auditory brain-computer interfaces, Nature Communications (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-39814-6
Journal information:
Nature Communications
Source: Read Full Article
