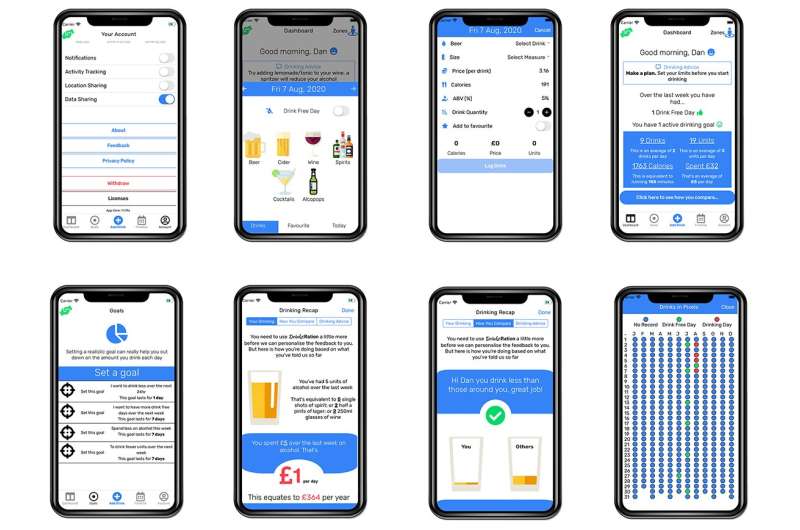
A new smartphone app, which has been made available to the public today, has been found to be successful in helping U.K. veterans to reduce alcohol consumption.
The 28-day brief alcohol intervention app was tested with more than 120 U.K. veterans as part of a trial funded by Forces in Mind Trust.
After using the Drinks:Ration app, veterans consumed 28 fewer units of alcohol (approximately 9 pints of standard U.K. beer) over a week than they had previously, compared with a control group who received only government advice on drinking alcohol, who consumed 10.5 fewer units of alcohol.
The app, developed by researchers at the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology and Neuroscience (IoPPN) at King’s College London, led by Dr. Daniel Leightley, and supported by Lancaster University and national veterans’ mental health charity Combat Stress, is designed to help people track their alcohol consumption.
Previous research has shown that alcohol misuse is higher in the U.K. Armed Forces than in the general population, and that this persists after an individual leaves service, particularly for those who are seeking help for a mental health condition. At present, no app exists in the United Kingdom that is designed to support the U.K. Armed Forces community to manage the amount of alcohol that they drink.
The app targets individual users’ motivations for drinking and promoting positive changes in behavior by using personalized messaging and data-driven infographics. The app is also designed to target shorter-term impacts of alcohol, such as the impact on relationships or finance and to provide daily personalized messaging. Most users taking part in this study were recruited from Combat Stress and had probable depression, anxiety, or posttraumatic stress disorder.
Following on from this successful trial, the U.K. Ministry of Defence, led by Surgeon Commander Kate King, will be trialing the Drinks:Ration app to assess its use and benefit to the serving community. The trial is due to start later this year.
“Our trial demonstrated that the Drinks:Ration app was effective in reducing alcohol misuse in help-seeking veterans in the medium term. This could make it a valuable tool for the Armed Forces community while they are waiting for treatment and support. This digital intervention could provide a novel, low-cost alternative to conventional help-seeking and be as effective as face-to-interventions. I am pleased that the U.K. Ministry of Defence will be undertaking a trial of the app with the serving community,” says Dr. Daniel Leightley, lead Researcher at the IoPPN, King’s College London.
“Our research shows that the Drinks:Ration app supported veterans to make positive changes to their patterns of drinking. We look forward to this app being rolled out more widely to support the veteran community,” says Prof Dominic Murphy, head of research at Combat Stress.
“We know from our research that veterans with a mental health problem often have co-occurring heavy drinking, yet this group can find it difficult to access the support that they need. This study has highlighted the positive benefits of providing digital support and how this could help to reduce alcohol use in veterans with co-occurring problems,” says Dr. Laura Goodwin, senior lecturer in mental health, Lancaster University.
“The team at King’s IoPPN have developed an effective short-term tool to lower harmful alcohol use in the Armed Forces Community, and to support veterans’ longer term positive mental health. It is important to note that not all veterans who experience problem drinking or mental health issues will seek help, and it is equally important to continue to find ways to reach out to those who could benefit from these kinds of interventions. The evidence is clear that this is an effective and low-cost tool to support veterans, and we look forward to seeing development of its further possibilities,” says Tom McBarnet, chief executive (acting), Forces in Mind Trust.
About the research
A “light” version of the Drinks:Ration app has been made available on Apple iOS and Google Android to the public today.
From a sample of 123 candidates, 62 were provided the intervention app and 61 were provided the control app. Both groups were administered a 28-day brief alcohol intervention delivered via their allocated smartphone app, with the objective of reducing self-reported alcohol consumption among U.K. veterans seeking help for mental health difficulties.
Source: Read Full Article
